Javascript 유효성 검사
1. Map이란?
Collection Framework에서 [Key, Value] 형태로 구성
2. Map과 JSON의 유사점
일반적으로 Javascript에서 사용하는 JSON 구조와 유사함
- Json 자료 예시

위의 자료는 Portfolio로 만들었던 웹사이트이다. Server 단에서 View 단으로 데이터를 전달할 때 JSON의 형태로 제공해준다. JSON 형태는 값을 가공하기 편해서 본인은 매우 선호하고 있음
‘w_no’는 Key, ‘5248’은 Value
3. Map의 조건
(1) Key값은 중복일 수 없음 (2) Key, Value 중 하나만 존재할 수 없음 (3) Value는 중복 가능
4. Map의 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Map<String, String> webtoonList = new HashMap<>();
webtoonList.put("w_no", "5248");
webtoonList.put("w_thumbnail", "https://~~~~");
webtoonList.put("w_seq", "3");
// Map의 제네릭의 타입을 두 개 넣을 수 있다.
// Key : String / Value : String 의미
// Map<String, Object> 또한 가능하다
5. Map의 종류
Map의 종류는 대표적으로 HashMap / TreeMap / LinkedHashMap이 있다.
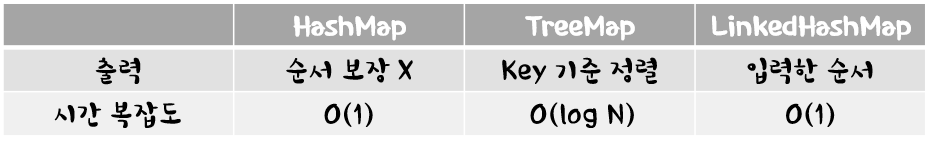
특별한 경우가 없다면, HashMap을 사용하도록 하자
6. Map의 사용법
- Put() / PutAll()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Map<String, Integer> fruits = new HashMap<>();
fruits.put("apple", 1);
fruits.put("banana", 2);
fruits.put("kiwi", 3);
fruits.put(null, 4);
fruits.put("kiwi", 5);
System.out.println("fruits: " + fruits);
// fruits: {banana=2, null=4, apple=1, kiwi=5}
Map<String, Integer> fruits = new HashMap<>();
fruits.put("apple", 1);
fruits.put("banana", 2);
fruits.put("kiwi", 3);
//PutAll()
Map<String, Integer> food = new HashMap<>();
food.put("coffee", 1);
food.put("hamburger", 2);
food.put("sandwich", 3);
//food <- fruits로 합치다(fruits에 있는 key/value를 food로 이동)
food.putAll(fruits);
System.out.println("food: " + food);
// food: {banana=2, apple=1, kiwi=3, coffee=1, sandwich=3, hamburger=2}
- get() / remove()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//get()
System.out.println("banana : "+food.get("banana"));
//banana : 2
//remove() : 해당 key값을 삭제하고 value값을 리턴
System.out.println("banana : "+food.remove("banana"));
//banana : 2
- containsKey() / containsValue()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//containsKey()
System.out.println("containsKey(apple): " + fruits.containsKey("apple"));
// containsKey(apple): true
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
//containsValue()
System.out.println("containsValue(1): " + fruits.containsValue(1));
// containsValue(1): true
- keySet(), values()
keySet() : Set 객체로 리턴 values() : Collection 객체로 리턴 ```java Map<String, Integer> fruits = new HashMap<>(); fruits.put(“apple”, 1); fruits.put(“banana”, 2); fruits.put(“kiwi”, 3);
//keyset()————————————- System.out.println(“keySet(): “ + fruits.keySet()); // keySet(): [banana, apple, kiwi]
Set
for (String key : keys) { System.out.println(“key: “ + key); } // key: banana // key: apple // key: kiwi
// values()————————————-
System.out.println(“values(): “ + fruits.values()); // values(): [2, 1, 3]
//Collection 타입으로 values 값을 넣어준다 Collection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
#### - replace()
```java
//값의 여부와 상관없이 시도함 / 삭제된 value return
public V replace(K key, V value)
System.out.println("replace(apple, 10): " + fruits.replace("apple", 10));
// replace(apple, 10): 1
System.out.println("replace(undefined, 10): " + fruits.replace("undefined", 10));
// replace(undefined, 10): null
//값이 일치한다면 시도함 / true or false return
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue)
System.out.println("replace(apple, 1, 10): " + fruits.replace("apple", 1, 10));
// replace(apple, 1, 10): true
System.out.println("replace(banana, 1, 10): " + fruits.replace("banana", 1, 20));
// replace(banana, 1, 10): false
7. 참고 사이트
참고 : codechacha.com